A mirror is a surface that reflects a clear image. An image that can be formed on the screen is known as a real image and the one which cannot be formed on the screen is known as a virtual image. These images are formed when light falls on a mirror from the object and is reflected back by the mirror on the screen. A mirror is a surface that reflects a clear image.
Images can be of two types:
1.Real image &
2.Virtual image.
An image that can be formed on the screen is known as a real image and the one which cannot be formed on the screen is known as a virtual image. These images are formed when light falls on a mirror from the object and is reflected back by the mirror on the screen.
Ray diagram helps to trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram used arrow type lines to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps to trace the direction in which light travels.
There can be two types of mirror: Curved mirror and plane mirror. If a curved mirror is a part of a sphere then it is known as a spherical mirror. The image formed by a plane mirror is always a virtual image as it cannot be obtained on a screen. The image formed by the spherical mirror can be either real or virtual. Spherical mirrors are of two types:
- Convex mirrors
- Concave mirrors
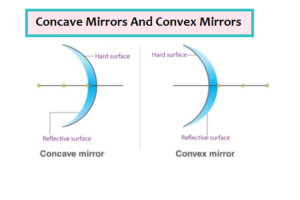
Concave Mirror |
Convex Mirror |
|
If a hollow sphere is cut into parts and the outer surface of the cut part is painted, then it becomes a mirror with its inner surface as the reflecting surface. This kind of mirror is known as a concave mirror. Light converges at a point when it strikes and reflects back from the reflecting surface of the concave mirror.
Hence, it is also known as a converging mirror. When the concave mirror is placed very close to the object, a magnified and virtual image is obtained. However, if we increase the distance between the object and the mirror then the size of the image reduces and a real image is formed. So, the image formed by the concave mirror can be small or large and it can also be real or virtual. |
If the other cut part of the hollow sphere is painted from inside, then its outer surface becomes the reflecting surface. This kind of mirror is known as a convex mirror. A convex mirror is also known as a diverging mirror as this mirror diverges light when they strike on its reflecting surface. Virtual, erect, and diminished images are always formed with convex mirrors, irrespective of the distance between the object and the mirror. Apart from other applications, the convex mirror is mostly used as a rearview mirror in vehicles. Spherical mirrors are the mirrors having curved surfaces that are painted on one of the sides. Spherical mirrors in which inward surfaces are painted are known as convex mirrors, while the spherical mirrors in which outward surfaces are painted are known as concave mirrors. Concave mirrors are also known as a converging mirror since the rays converge after falling on the concave mirror, while the convex mirrors are known as diverging mirrors as the rays diverge after falling on the convex mirror. In this article, we will learn about image formation by concave and convex mirrors. |
Guidelines for Rays Falling on the Concave and Convex Mirrors
- When a ray strikes concave or convex mirrors obliquely at its pole, it is reflected obliquely.
- When a ray, parallel to principal axis strikes concave or convex mirrors, the reflected ray passes through the focus on the principal axis.
- When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex mirrors, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis.
- A ray passing through the center of curvature of the spherical mirror will retrace its path after reflection.
Image Formation By Concave Mirror
By changing the position of the object from the concave mirror, different types of images can be formed. Different types of images are formed when the object is placed:
- At the infinity
- Beyond the center of curvature
- At the center of curvature
- Between the center of curvature and principal focus
- At the principal focus
- Between the principal focus and pole
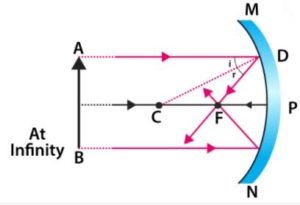
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram
- Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object.
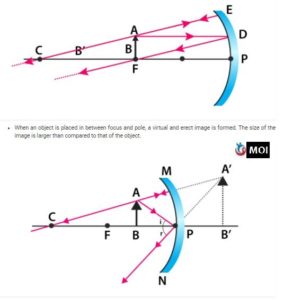
- When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. The size of the image is smaller than compared to that of the object.

- When an object is placed at the center of curvature and focus, the real image is formed at the center of curvature. The size of the image is the same as compared to that of the object.

- When an object is placed at the focus, the real image is formed at infinity. The size of the image is much larger than compared to that of the object.
Summary
| S. No | Position of Object | Position of Image | Size of Image | Nature of Image |
| 1 | At infinity | At the focus F | Highly Diminished | Real and Inverted |
| 2 | Beyond the center of curvature C | Between F and C | Diminished | Real and Inverted |
| 3 | At the center of curvature C | At C | Same Size | Real and Inverted |
| 4 | Between C and F | Beyond C | Enlarged | Real and Inverted |
| 5 | At focus F | At Infinity | Highly Enlarged | Real and Inverted |
Image Formation By Convex Mirror
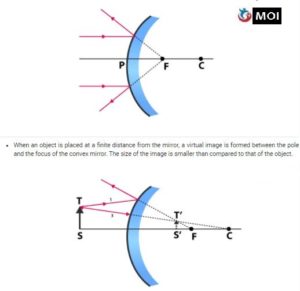
The image formed in a convex mirror is always virtual and erect, whatever be the position of the object. In this section, let us look at the types of images formed by a convex mirror.
- When an object is placed at infinity, a virtual image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than compared to that of the object.
Summary
| S. No | Position Of Object | Position of Image | Size of Image | Nature of Image |
| 1 | At Infinity | At the focus F, behind the mirror | Highly diminished | Virtual and Erect |
| 2 | Between Infinity and the Pole | Between P and F, behind the mirror | Diminished | Virtual and Erect |